All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Knowledge and Practice of the Different Maxillofacial Prostheses among Sudanese Dental Practitioners: A Cross-sectional Study
Abstract
Objective
This study aims to assess the knowledge and practice of different types of maxillofacial prosthetic devices among Sudanese dental practitioners.
Materials and Methods
A descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted in the main governmental dental hospital, Khartoum Dental Teaching Hospital, and the Faculty of Dentistry, University of Khartoum. A self-administered questionnaire consisting of 23 closed questions addressing the participant’s socio-demographic data, knowledge, and practice of maxillofacial prostheses was conducted and distributed. One hundred and eighteen specialists and residents of multidiscipline were enrolled voluntarily, excluding prosthodontists, using the stratified sampling technique and simple randomization within the stratum. The participant's knowledge and practice were calculated as percentages achieved by dividing the number of accurate answers by the total number of questions and hence categorized as good 66.6%–100%, average 33.3%–66.6%, and poor less than 33.3%. The data was collected and analyzed using the IBM Statistical Package.
Results
The overall knowledge score was average, with a significant association between the different specialties. While the practice score was poor, there was a significant relationship between the participant’s knowledge and their practice (p = 0.001*). The majority of respondents, 80.5% and 68.6%, reported that the lack of knowledge and the multidisciplinary approach in the treatment of maxillofacial patients were the main barriers that prevented the use of the different maxillofacial prostheses. A high percentage (83.1% of respondents) recommended improving awareness and training, and 78% highlighted the application of the multidisciplinary approach and recommended a specialized treatment protocol.
Conclusion
Although the participants had an average knowledge of the different maxillofacial prostheses, their practice was poor. The lack of knowledge and training and the absence of a multidisciplinary team have been highlighted as the main barriers that prevent the use of the different maxillofacial prostheses.
Clinical Significance
Maxillofacial prostheses play a crucial role in rehabilitating patients with maxillofacial defects by improving the patient’s aesthetics, phonetics, masticatory efficiency, self-esteem, and quality of life. Hence, dental practitioners' knowledge and practice of the different maxillofacial prostheses are of great importance.
1. INTRODUCTION
Maxillofacial deformities caused by resection, trauma, and congenital illnesses can cause significant facial disfigurements, functional difficulties, and psychological consequences that influence the patient’s health and quality of life [1-3].
Several treatment modalities have been described to rehabilitate maxillofacial defects, including surgical and prosthetic treatment modalities [1-3]. Despite advance- ments in surgical modalities, significant defects cannot be satisfactorily rehabilitated using surgical techniques alone, increasing the demand for maxillofacial prosthetic rehabilitation [3-5]. Moreover, the prosthetic treatment showed many advantages, including reducing the treatment time, providing transitional treatment, and reducing cost [1, 6, 7].
According to the Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms [4], a Maxillofacial prosthesis is any prosthesis used to replace part or all of any stomatognathic and/or craniofacial structures [4]. These prosthetic devices play a significant role in improving the patient’s quality of life by restoring their aesthetic, functional, and psychological demands [3]. Thus, the multidisciplinary treatment approach and the close communication between the different maxillofacial team members are crucial and play a significant role in the success of the treatment [1, 2, 6-9]. All the team members should collaborate to bring out the best standard of health care for the patient, which necessitates a satisfactory level of knowledge about the different prosthetic appliances that can be used in rehabilitating different maxillofacial patients.
In a survey conducted by Jain et al. [1] among undergraduate dental students at the AIMST Dental Institute, Malaysia, a high percentage of dental students (69%) reported their awareness about prosthetic rehabilitation as an alternative treatment option for plastic reconstructive surgery. Forty–five percent of the respondents in a survey conducted by Wolfaardt et al. [10] highlighted the increasing demands for maxillofacial prosthodontics in the past 10 years in North America, and 42% emphasized that more maxillofacial prostheses have been requested in their areas [10].
Elbashti et al. [11] conducted a study reviewing the future of maxillofacial prosthodontics as a subspecialty in Libya. They reported that although this subspecialty is widely recognized in developed countries, it is less applicable in many developing countries, emphasizing the need for short- and long-term enhancement protocols [11].
Despite the advantages of the different maxillofacial prostheses, limited data on their use in Sudan were reported [1, 6, 7]. This study aims to assess the knowledge and practice of different dental practitioners, including Maxillofacial Surgeons, Pedodontists, orthodontists, periodontists, and restorative specialists, about the different maxillofacial prostheses and their uses and to identify the obstacles that prevent the practice of the different maxillofacial prostheses.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
The research was registered with the Ethical Committee (No. IRB/KTDH/2021/0018) of the Khartoum Teaching Dental Hospital and Faculty of Dentistry, University of Khartoum, prior to the commencement of the study. The study was conducted between June 2021 and January 2023. Each participant signed an informed consent form before enrolment.
2.1. Sample Selection and Sample Size Calculation
The study population included all the restorative, peadodontists, periodontists, orthodontists, and oral maxillofacial surgeons at the University of Khartoum, Faculty of Dentistry, and Khartoum Dental Teaching Hospital, which were divided into clusters according to their specialty. The dental house officers, the prostho- dontists, and the participants who did not sign the informed consent were excluded. The total population was found to be 167, as demonstrated in Table 1.
To satisfy the objective of the study, the sample size was determined using the following formula:
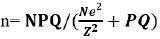 |
Where:
n= the sample size. N: population. e: significant level.
For this study, we assumed: e = 0.05. N = Total population. = 167.
Applying the above formula, the sample size was 118 participants.
The number of respondents needed from each specialty had been calculated with a probability proportional to the population size of each specialty, with Simple randomization for sample allocation within the strata (Table 1).
2.2. Questionnaire Design
A self-administered questionnaire, written in English, including a validated set of 23 closed-ended questions modified from previously validated questionnaires [1, 12-14], was distributed to the participants to be completed voluntarily within 1 week.
The questionnaire had three sections: The first section was designed to include the participants' demographic characteristics. The second section of the questionnaire consists of questions aimed at assessing the necessary knowledge regarding maxillofacial appliances based on previous studies [1, 12-14]. The third section of the questionnaire, designed by the author, includes questions targeting the participants' practice regarding the different maxillofacial appliances and the barriers that prevent their use [1, 3, 11].
2.3. The Participant’s Knowledge and Practice Scores
The participant’s knowledge and practice scores were calculated as percentages achieved by dividing the number of accurate answers by the total number of questions and categorized into good (66.6–100%), average (33.3–66.6%), and poor (less than 33.3%).
2.4. Reliability and Validity of the Questionnaire
A pilot study was carried out among 35 participants using the convenience sampling technique. The questionnaire was administered twice at 2-week intervals to test its reliability using Cronbach’s test, which was found to be 0.6, which is considered reliable. Moreover, three experts assessed the validity, internal consistency, acceptability of the time needed to complete the questionnaire, and the questions’ clarity, and it was found valid and provided adequate information and results.
2.5. Data Analysis
The data were collected, coded, tabulated, and statistically analyzed using the IBM Statistical Package for Social Sciences software, SPSS version 22. Tables, graphs, means, frequencies, and standard deviations were used for descriptive statistics. The Chi-square test was used to analyze the data. A p-value of 0.05 was considered significant, with a 95% confidence interval.
The pilot study data was not included in the research statistics.
3. RESULTS
3.1. Participants Characteristics
One hundred eighteen questionnaires were distributed and were fully answered with a response rate of 100%. Out of the 118 participants, fifty-one (43.2%) were males and sixty-seven (56.8%) were females, with a high-frequency age group between 30-39 years, including 75 subjects (63.6%) (Table 2).
Most of the participants were BDS holders (50 subjects, 42.4%). While only 9 participants (7.6%) were Ph.D. holders, as shown in Table 2. Considering the participants’ specialties, the majority of the participants were the registrars of maxillofacial surgery (28, 23.7%) and periodontology (20, 16.9%) (Table 2).
| Sample (Participants) Distribution | Population Size | Sample Size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Maxillofacial Surgeon | Specialists | 20 | 14 |
| Residents | 40 | 28 | |
| Restorative | Specialists | 8 | 6 |
| Residents | 26 | 18 | |
| Periodontists | Specialists | 13 | 9 |
| Residents | 28 | 20 | |
| Peadodontists | Specialists | 4 | 3 |
| Residents | 8 | 6 | |
| Orthodontists | Specialists | 8 | 6 |
| Residents | 12 | 8 | |
| Total | 167 | 118 | |
| Variable | Frequency | Percent (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 51 | 43.2% |
| Female | 67 | 56.8% | |
| Age | Less than 30 years | 26 | 22% |
| 30-39 years | 75 | 63.6% | |
| 40-49 years | 12 | 10.2% | |
| 50 years and above | 5 | 4.2% | |
| Academic Qualification | BDS | 50 | 42.4% |
| MDS | 19 | 16.1% | |
| MSc | 40 | 33.9% | |
| PhD | 9 | 7.6% | |
| The participants’ specialty | Maxillofacial Surgery | 42 | 35.6% |
| Orthodontics | 14 | 11.9% | |
| Periodontists | 29 | 24.6% | |
| Peadodontists | 9 | 7.6% | |
| Restorative | 24 | 20.3% | |
Table 3.
| Variable | Frequency | Percent (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge about maxillofacial defects and prostheses | Undergraduate | 52 | 44.1% |
| Postgraduate | 51 | 43.2% | |
| Both | 15 | 12.7% | |
| Total | 118 | 100% | |
| The different maxillofacial defects seen by the participants during their practice | Cleft lip and palate | 102/118 | 86.4% |
| Acquired maxillary defect | 66/118 | 55.9% | |
| Acquired mandibular defect | 59/118 | 50% | |
| Both maxillary and mandibular defects | 50/118 | 42.3% | |
| Facial defect | 49/118 | 41.5% | |
| I haven’t seen such a patient | 9/118 | 7.6% | |
| The different causes of the maxillofacial defects | Congenital disorders | 102/118 | 86.4% |
| Tumour resection | 100/118 | 84.7% | |
| Trauma | 92/118 | 78% | |
| Developmental disorders | 78/118 | 66.1% | |
| Cyst enculation | 51/118 | 43.2% | |
| Infections | 49/118 | 41.5% | |
| No definitive cause | 9/118 | 7.6% | |
| I don’t know | 1/118 | 0.85% | |
| The disabilities associated with the maxillofacial defects | Difficulties during eating and swallowing. | 113 | 95.8% |
| Difficulties with speech and phonation | 111 | 94.1% | |
| Disfigured appearance | 104 | 88.1% | |
| Psychological disturbance | 88 | 74.5% | |
| Poor oral hygiene | 82 | 69.5% | |
| Trismus | 59 | 50% | |
| Hypersalivation | 59 | 50% | |
| Hyposalivation | 18 | 15.2% | |
| Treatment modalities used for maxillofacial defects | Either surgical or prosthetic treatment can be used | 15/118 | 13.8% |
| Both surgery and prosthesis | 100/118 | 84.7% | |
| I have no idea | 3/118 | 2.5% | |
| The multidisciplinary Clinic/Meeting | Yes | 45 | 38.1% |
| No | 46 | 39% | |
| I am not sure | 27 | 22.9% | |
| Total | 118 | 100% | |
| The Multidisciplinary team members | Oral-Maxillofacial Surgeon | 42/118 | 35.6% |
| Prosthodontist | 37/118 | 31.4% | |
| Peadodontist | 13/118 | 11% | |
| Periodontist | 14/118 | 11.9% | |
| Orthodontist | 23/118 | 19.5% | |
| Speech Therapist | 15/118 | 12.7% | |
| Plastic surgeon | 16/118 | 13.6% | |
| ENT surgeon | 16/118 | 13.6% | |
| Dental technician | 17/118 | 14.4% | |
| Social Worker | 8/118 | 6.8% | |
| Medical oncologist | 7/118 | 5.9% | |
| Psychologist | 15/118 | 12.7% | |
Fifty-two (44.1%) of the participants knew about maxillofacial defects during their postgraduate periods. While fifty-one (43.2%) knew during undergraduate study. Moreover, 102 participants (86.4%) met cleft lip and palate patients during their practice, while only 9 (7.6%) of the participants reported that they hadn’t seen a patient with maxillofacial defects (Table 3).
Most of the respondents declared that congenital disorders and tumor resection were the main causes of maxillofacial defects, with 86.4% and 84.7%, respectively. On the other hand, only one respondent mentioned that they have no idea about the causes of maxillofacial defects (Table 3).
The majority of the participants identified difficulties during eating, swallowing, and speech (95.8% and 94.1%, respectively) as one of the disabilities associated with maxillofacial defects, followed by disfigured appearance (88.3%) (Table 3).
The majority of respondents (100,84.7%) mentioned that both surgical and prosthetic reconstructions are the best treatment modalities for a patient with a significant maxillary defect. In comparison, 3 respondents (2.5%) reported a lack of knowledge regarding the different treatment modalities (Table 3).
Forty-six (39% of the respondents) declared that there is no multidisciplinary clinic meeting held at the institutes where they work to discuss the comprehensive treatment plan for maxillofacial patients, while 45 (38.1%) of participants have those meetings (Table 3).
Most participants who knew about the team recognized the oral-maxillofacial surgeon’s specialties and the prosthodontists at 35.6% and 31.4%, respectively (Table 3).
3.2. Knowledge of the Participants about the Different Maxillofacial Prostheses
The majority of participants considered that the obturator and the feeding appliance are the most common maxillofacial prostheses that can be used in cases with congenital cleft lip and palate (66.1% and 63.6%, respectively). On the other hand, only 3 participants (2.5%) reported their level of knowledge (Table 4).
A high percentage of the participants, 83.9% of the 99 subjects, declared that the maxillofacial prostheses used in cases with acquired maxillary defects are obturators. At the same time, 44 participants (37.3%) stated that implant-supported reconstructive prosthesis is one of the treatment options. Only 4 participants, or 3.4%, had no idea (Table 4).
The majority of respondents, 63 (53.4%), considered that the maxillofacial prostheses used in cases with acquired mandibular defects are implant-supported reconstructive prostheses, while 56, or 47.5%, confirmed the use of mandibular guidance appliances. Moreover, 12.2% of subjects reported their level of knowledge (Table 4).
Fifty-seven participants (48.3%) recognized using a maxillofacial stent as implant guidance. 33,28% knew the use of it as a mouth guard, and 34,28.8% knew the fixation of a fractured jaw. On the other hand, 9 participants (7.6) reported their lack of knowledge about the maxillofacial stent (Table 4).
Seventy-six out of all the respondents, 64.4%, recognized that maxillofacial splints could be used to fix the fractured jaw, while 29.6%, or 24.6%, stated they had no idea about the uses of maxillofacial stents (Table 4).
Most of the respondents, 81.4%, were familiar with acrylic resin as the material of choice for constructing maxillofacial prostheses. On the other hand, 13 declared their lack of knowledge (Table 3).
| Variable | Frequency | Percent (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge about different maxillofacial prostheses that can be used in cases with congenital cleft lip and palate | Obturator | 78 | 66.1% |
| Feeding appliance | 75 | 63.6% | |
| Nasopharyngeal obturator | 31 | 26.2% | |
| Palatal lift prosthesis | 27 | 22.9% | |
| Implant supported reconstructive prosthesis | 26 | 22% | |
| Expansion type prosthesis | 26 | 22% | |
| Splint prosthesis | 15 | 12.7% | |
| Eruption stent | 5 | 4.2% | |
| Cranial prosthesis | 5 | 4.2% | |
| Mandibular guidance appliances | 5 | 4.2% | |
| Meatus prosthesis | 3 | 2.5% | |
| Fluoride stent | 3 | 2.5% | |
| I have no Idea | 3 | 2.5% | |
| Knowledge about the different maxillofacial prostheses that can be used in cases with acquired maxillary defects | Obturator | 99 | 83.9% |
| Implant supported reconstructive prosthesis | 44 | 37.3% | |
| Speech aids prosthesis | 24 | 20.3% | |
| Palatal lift prosthesis | 19 | 16.1% | |
| Splint prosthesis | 18 | 15.3% | |
| Feeding appliance | 14 | 11.9% | |
| Cranial prosthesis | 9 | 7.6% | |
| Mandibular guidance appliances | 6 | 5.1% | |
| Fluoride stent | 4 | 3.4% | |
| Meatus prosthesis | 3 | 2.5% | |
| Eruption stent | 2 | 1.7% | |
| I have no Idea | 4 | 3.4% | |
| Knowledge about the different maxillofacial prostheses that can be used in cases with mandibular defects | Implant supported reconstructive prosthesis | 63 | 53.4% |
| Mandibular guidance appliances | 56 | 47.5% | |
| Obturator | 24 | 20.3% | |
| Surgical stent | 21 | 17.8% | |
| Splint prosthesis | 18 | 15.3% | |
| Expansion type prosthesis | 15 | 12.7% | |
| Feeding appliance | 12 | 10.2% | |
| Speech aids prosthesis | 10 | 8.5% | |
| Meatus prosthesis | 3 | 2.5% | |
| I have no Idea | 12 | 10.2% | |
|
Knowledge about the different uses of maxillofacial Stents |
Implant guidance | 57 | 48.3% |
| Carry medication | 37 | 31.4% | |
| Fixation of fracture jaw | 34 | 28.8% | |
| Mouth Guard | 33 | 28% | |
| Protect the teeth during sport | 28 | 23.7% | |
| Vestibuloplasty | 28 | 23.7% | |
| Protect the teeth and soft tissue in patient with bruxism | 26 | 22% | |
| Protection from radiation therapy | 23 | 19.5% | |
| Periodontal purpose | 17 | 14.4% | |
| Control the bleeding in hemophilic patient | 16 | 13.6% | |
| Cosmetic reason | 15 | 12.7% | |
| I have no idea | 9 | 7.6% | |
| Dislocation treatment | 6 | 5.1% | |
| Help in teeth eruption | 5 | 4.2% | |
| Drainage of periapical infection | 2 | 1.7% | |
| Knowledge about the different uses of maxillofacial Splints | Fixation of fracture jaw | 76 | 64.4% |
| I have no idea | 29 | 24.6% | |
| Protect the teeth during sport | 21 | 17.8% | |
| Cosmetic reason | 16 | 13.6% | |
| Periodontal purpose | 13 | 11% | |
| Protect the teeth and soft tissue in patient with bruxism | 11 | 9.3% | |
| Implant guidance | 10 | 8.5% | |
| Mouth Guard | 10 | 8.5% | |
| Vestibuloplasty | 4 | 3.4% | |
| Protection from radiation therapy | 4 | 3.4% | |
| Help in teeth eruption | 4 | 3.4% | |
| Carry medication | 3 | 2.5% | |
| Control the bleeding in hemophilic patient | 3 | 2.5% | |
| Drainage of periapical infection | 0 | 0% | |
| Knowledge about the different materials that used for the construction of Maxillofacial Prostheses | Chrome Cobalt (Cr-Co) | 59 | 50% |
| Wax | 8 | 6.8% | |
| Acrylic resin | 96 | 81.4% | |
| Gypsum | 4 | 3.4% | |
| Silicone | 26 | 22% | |
| I don’t know | 13 | 11% | |
| The participant’s Self- evaluation about their knowledge about the maxillofacial prosthesis | Excellent | 0 | 0% |
| Good | 43 | 36.4% | |
| Poor | 71 | 60.2% | |
| No knowledge | 4 | 3.4% | |
| Total | 118 | 100% | |
| Referred and/or treated a patient with a maxillofacial prosthesis during their practice | Yes | 64 | 54.2% |
| No | 54 | 45.8% | |
| Total | 118 | 100% | |
| Number of maxillofacial prostheses performed or requested by the participants during their work | 1-5 cases | 43/64 | 67.2% |
| 5-10 cases | 7/64 | 10.9% | |
| More than 10 cases | 14/64 | 21.9% | |
| Total | 64 | 100% | |
| The Barriers that prevent the participants from constructing the maxillofacial prostheses | Lack of knowledge | 95/118 | 80.5% |
| Lack of the multidispinary approach of treatment | 81/118 | 68.6% | |
| Lack of funding. | 43/118 | 36.4% | |
| Lack of time | 13/118 | 11% | |
| The recommendations of the participants | Improve the awareness and training | 98/118 | 83.1% |
| Application of the multidispinary approach of treatment | 92/118 | 78% | |
| Need of a specialized center | 73/118 | 61.9% | |
| Financial support | 58/118 | 49.2% | |
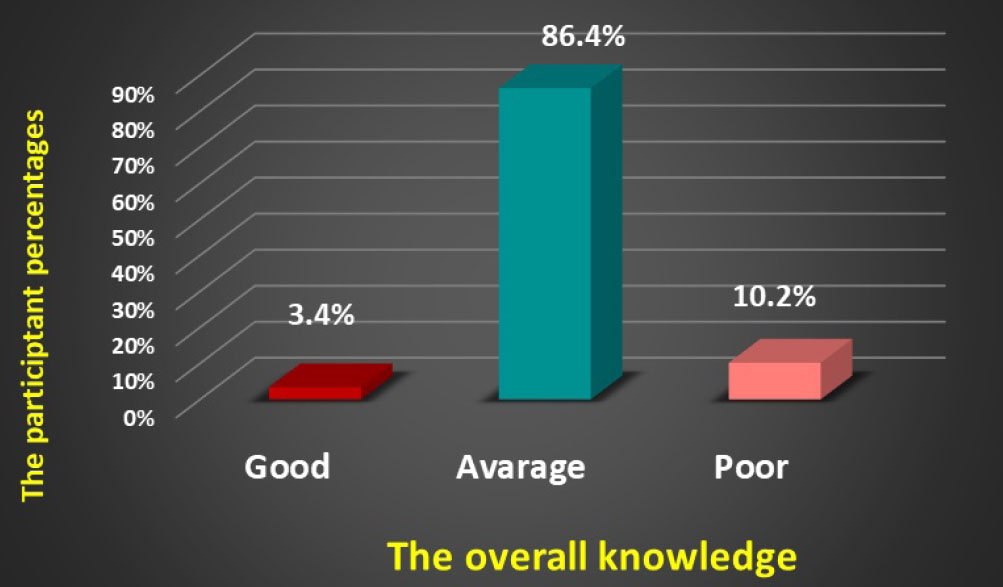
The overall knowledge score of the participants about maxillofacial prostheses.
More than half of the respondents (71, 60.2%) self-evaluated their knowledge about maxillofacial prostheses as poor. No one reported excellent knowledge evaluation (Table 4).
Sixty-four of the participants (54.2%) declared that they had referred and/or treated a patient with a maxillofacial prosthesis during their practice, while 54.8% had not (Table 4).
Out of the 64 participants who have treated and/or referred patients with maxillofacial defects, 36.4% requested 1–5 devices, 5.9% requested 5–10, and the rest, 11.9%, requested more than 10 (Table 4).
The majority of respondents, 80.5%, reported that a lack of knowledge and the lack of a multidisciplinary approach to treatment. 68.6% of maxillofacial patients reported the main barriers that prevented the use of different maxillofacial prostheses (Table 4).
A high percentage, 83.1%, recommend improving awareness and training, while others, by a percentage of 78%, advise the application of the multidisciplinary approach to treatment to include the maxillofacial prosthesis within the maxillofacial patient treatment protocol (Table 4).
Almost all the respondents (95.8%) recommended the conduct of a recognized maxillofacial prosthetic program to support healthcare professionals in managing maxillofacial defects (Table 4).
When evaluating the level of the participants’ knowledge about the different maxillofacial prostheses, the results of this study revealed that the majority of the participants, 86.4%, revealed an average level of knowledge score of 33%–66% (Fig. 1): Poor knowledge was reported with the maxillofacial prostheses used in patients with cleft lip and palate, maxillary defects, and stents: 62.7%, 88.1%, and 84.7%. On the other hand, the participants reported good knowledge of maxillofacial splint prostheses and average knowledge concerning mandibular defect prostheses.
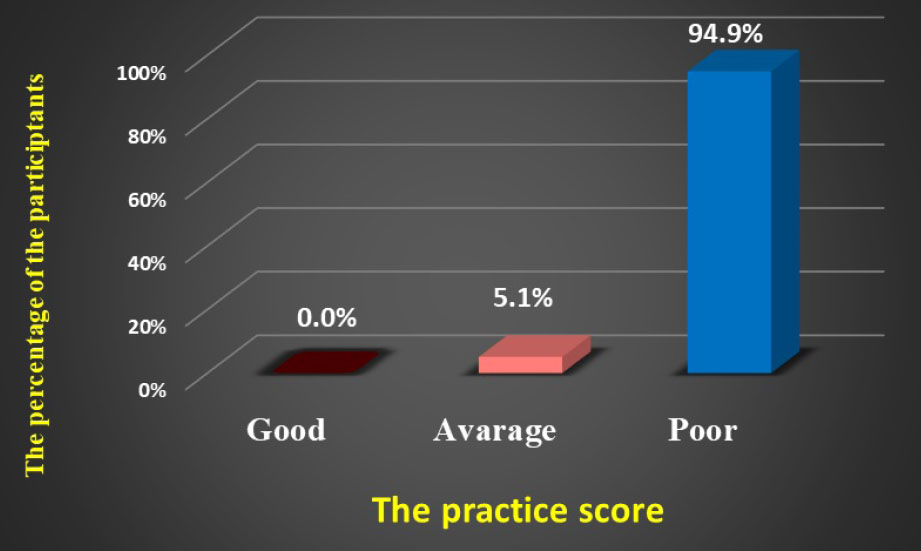
The overall practice score of the participants about the maxillofacial prostheses.
| knowledge | Good | Average | Poor | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxillofacial Surgery | n | 2 | 38 | 2 | 42 |
| % | 4.8% | 90.5% | 4.8% | 100% | |
| Orthodontics | n | 2 | 12 | 0 | 14 |
| % | 14.3% | 85.7% | 0% | 100% | |
| Periodontists | n | 0 | 26 | 3 | 29 |
| % | 0% | 89.7% | 10.3% | 100% | |
| Peadodontists | n | 0 | 8 | 1 | 9 |
| % | 0% | 88.9% | 11.1% | 100% | |
| Restorative | n | 0 | 18 | 6 | 24 |
| % | 0% | 75% | 25% | 100% | |
| Total | n | 4 | 102 | 12 | 118 |
| % | 3.4% | 86.4% | 10.2% | 100% | |
| - | Average Practice | Poor Practice | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Good Knowledge | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| 75% | 25% | 100% | |
| Average Knowledge | 3 | 99 | 102 |
| 2.9% | 97.1% | 100% | |
| Poor Knowledge | 0 | 12 | 12 |
| 0% | 100% | 100% | |
| Total | 6 | 112 | 118 |
| 5.1% | 94.9% | 100% |
Moreover, there is a significant positive relationship between the participants' specialty and their knowledge. (P value = 0.049*). The orthodontists showed a higher percentage of good knowledge (Table 5).
When evaluating the level of participant practice of the maxillofacial prostheses, the results of this study revealed that the majority of the participants (94.9%) reported a poor level of practice. 0%-33%, with none of the participants showing good practice (0%) (Fig. 2).
A significant relation was reported between the participant’s knowledge and their practice using the Chi-Square test (P value = 0.001*). Participants with poor knowledge had no practice at all, while those with average knowledge reported a poor practice score of 97.1% (Table 6).
4. DISCUSSION
Maxillofacial defects following tumor resection, trauma, and congenital disorders may result in significant facial disfigurements, multiple functional disabilities (phonation, mastication), and psychological consequences that affect the patient’s health and quality of life [1-3]. Despite the noteworthy improvements in the surgical approach to managing oral and facial defects, it has been found that significant defects cannot be satisfactorily managed by plastic surgery alone [3]. Hence, the need for maxillofacial prostheses has greatly increased, especially in the last few years.
Maxillofacial prosthesis is any prosthesis used to replace part or all of any stomatognathic and/or craniofacial structures [4]. It plays a significant role in restoring hard and soft tissues and rehabilitating the function and appearance of maxillofacial patients. Thus, the multidiscipline of dentistry must include adequate knowledge about the various types of devices and understanding of the uses of these devices to help patients regain their lives and improve their quality of life.
To our knowledge, this study is the first to assess the knowledge and practice of the different dental practitioners—maxillofacial surgeons, pedodontists, ortho- dontists, periodontists, and restorative specialists—about the different maxillofacial appliances and their uses.
The majority of the participants in this study were female, reflecting an increased number of female dental practitioners compared to male ones. The same observation was remarked by Fotedar et al. [15] in India, who conducted a study to assess undergraduate dental students' knowledge, attitude, and practices about oral cancer, and an increase in female dental professionalism and practice was noticed. The same observation was reported by Jain et al [1].
Most participants declared that they learned about maxillofacial prostheses from their academic studies. While the remaining mentioned that the source of their information was books, journals, referral doctors, and the internet, this high result can be related to the academic status of the participants, as they were post-graduate students and specialists. This result is in line with Mariona et al. [14], who affirmed that most of their respondents heard about maxillofacial prostheses in their 3rd year of study.
On the other hand, a survey conducted by Jain et al. [1] among undergraduate participants showed that 90% were aware of the maxillofacial prosthesis through newspapers and magazines. The differences in the results can be related to the academic status of the participants.
In the same vein, Berge [16] stated that the media was the primary source of information about maxillofacial prosthetics.
In the present study, most of the participants were residents and consultants, except for prosthodontists, who had a range of experiences ranging from a minimum of one year to a maximum of 35 years. Nearly half of the participants declared the absence of a multidisciplinary team in their practice. In contrast, Suhaimi A [17]. stated that more than half of Malaysian and New Zealand respondents in their study reported the availability of multidisciplinary meetings and treatment approaches at their centers to treat oral cancer patients. In a study conducted by Suliman R and Awadalkreem F [8] in Sudan, the majority of participants stated that there is no specific protocol used for the management of maxillofacial patients.
In the same line, Hubálková et al. [5] emphasized the importance of maxillofacial team members to optimize the treatment of maxillofacial patients, restore the patient’s function, aesthetics, and psychology, and improve the patient’s quality of life [5]. Whereas, Meenakshi and Shah [18] published an article highlighting that managing patients with maxillectomy requires a multidisciplinary approach.
When considering the suitable treatment modality for significant maxillary defects, most respondents agreed that surgery and prosthetic replacement are the treatment modality of choice. This result is in line with Ariani N et al. [2] and Hubálková et al. [5], who recommended the teamwork approach to optimize the treatment outcome and provide the patient with a standard of care.
Participants in the present study believed that maxillofacial surgeons and prosthodontists are the significant specialties involved in treating maxillofacial defects. In accordance with this, Sivanagini et al. [19] reported that the maxillofacial rehabilitating team for the patient with a cleft lip and palate may include the following specialists: ENT surgeon, genetic scientist, plastic and oral surgeon, orthodontist, prosthodontist, pedodontist, ophthalmologist, psychiatrist, speech thera- pist, nursing support, and social worker.
When asking the participants about the types of defects they came across during their practice, most of the respondents had seen a variety of defects, including cleft lip and palate, acquired maxillary and mandibular defects, and facial defects. In contrast, the minority has not seen any maxillofacial cases. This evidence highlights the high prevalence of oral congenital and acquired defects and necessitates the importance of knowledge about maxillo- facial appliances, as emphasized by Duni et al. [20].
In contrast, although 68% of the participants in a study conducted by Mariona et al. [14] have heard of the term obturator, 75% of them have not come across any patient who needs an obturator.
In the same vein, Karthikeson et al. [21] reported that the majority of the respondents in their study were aware of the maxillofacial prosthesis.
Moreover, Duni et al. [20] recommended that every dentist should identify and know how to construct maxillofacial prostheses to rehabilitate suffering patients.
The participants were asked about the types of defects they came across. They responded that they had seen a variety of defects, including cleft lip and palate, acquired maxillary and mandibular defects, and facial defects, while the minority had not seen any. This highlights that oral congenital and acquired defects have a high prevalence, which necessitates the importance of knowledge about maxillofacial appliances, as emphasized by Duni et al. [20], a result that antagonized the previously reported by Mariona et al. [14]
Disabilities associated with maxillofacial defects, including difficulties with eating, swallowing, speech, phonation, disfigurement, and poor oral hygiene, were all identified by the participant and matched what had been reported by Jain A et al. [1] and Karthik et al. [3].
The result of the present study rated the awareness of the different types of maxillofacial prostheses as average. A result that matched Mariona et al. [14] investigated the knowledge and practice of obturators among dental students in Chennai using a cross-sectional questionnaire. The investigators found that the participants' level of awareness about obturators was moderate.
In a study by Karthikeson et al. [21], most respondents reported their awareness of maxillofacial prostheses. Eighty-five of the dentists, including in the study conducted by Sivanagini et al. 19 regarding the feeding appliance, declared that they receive a frequency of cases with orofacial clefts of around 10 cases within a six- month’s period of time. Almost half of the participants reported that they had treated [1-5] cases of maxillofacial patients until the completion of the survey. Moreover, almost half of the participants do not receive maxillofacial patients; this can be attributed to the lack of a multidisciplinary team approach and a specialized center for managing patients with maxillofacial defects.
The majority of respondents stated that they had not treated or referred patients with a maxillofacial prosthesis. Despite differences in the participants' academic status between the two studies, this result is consistent with what Mariona et al. [14] reported. In the same vein, Kumar et al. [22] stated that although the obturator prosthesis has a high positive impact on the patient's quality of life, half of the participants in their study did not treat such patients.
Most of the participants emphasized that a lack of knowledge and a lack of a multidisciplinary treatment approach were the main barriers preventing the use of different types of maxillofacial prostheses. Suliman R. and Awadalkreem F [8] reported with the same result This result underlines the urgent demand to improve know- ledge and practice about the different types of maxillofacial prostheses and their broad spectrum of uses. This need has been supported by Elbashti et al. [11] who considered maxillofacial prosthetics to be a subspecialty of prosthodontics with a relatively broad scope that provides prosthetic rehabilitation and therapeutic appliances for numerous disorders, injuries, and defects of the head and neck region.
Most participants recommended improving their awareness and training, applying the multidisciplinary treatment approach, and requesting a specialized center and financial support. These recommendations were supported by Meenakshi et al. [18], who highlighted the multidisciplinary team's role in managing patients with maxillectomy.
Almost all the participants underlined the need to conduct a recognizable maxillofacial prosthetic program to support healthcare professionals in managing patients with maxillofacial defects and to provide a standard of care treatment for these patients. Elbashti et al. [11] highlighted the need for the development of an urgent short-term plan and a long-term institutional plan for establishing a maxillofacial prosthetics program in Libya.
These recommendations matched the previous evidence of data concerning the knowledge of nurses, dentists, and dental students about oral cancer and its management in general, as reported by Fotedar et al. [15] and Patel et al. [23].
The limitation of this study was the relatively limited study area.
CONCLUSION
Within the limitations of this study, an average level of knowledge regarding the different types of maxillofacial prostheses was reported, with a poor level of practice. The consultants and residents of maxillofacial surgeons had a higher knowledge level than other specialties. The lack of knowledge and training and the lack of a multidisciplinary team are the main barriers that prevent the use of different maxillofacial prostheses.
The necessity of conducting a recognized maxillofacial prosthetic program to improve the knowledge, practice, and support of healthcare providers in managing maxillofacial defects has been highlighted.
AUTHORS’ CONTRIBUTION
Sahar Ahmed was responsible for the conception and design of the study, the acquisition of data, and the drafting of the paper; Fadia Awadalkreem was involved in the conception and design of the study, the critical revision of the questionnaire, the analysis and interpretation of the data, and the drafting and reviewing of the paper; and Kusai Baroudi was involved in the analysis and interpretation of the data, and the final editing and reviewing of the paper.
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
The research was registered with the Ethical Committee (No. IRB/KTDH/2021/0018) of the Khartoum Teaching Dental Hospital and Faculty of Dentistry, University of Khartoum, prior to the commencement of the study.
HUMAN AND ANIMAL RIGHTS
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of institutional and/or research committees and with the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki, as revised in 2013.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
The data and supportive information are available within the article.


