All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Measuring Patient’s Orofacial Estheticsin in Prosthodontics: A Scoping Review of a Current Instrument
Abstract
Objective:
Although prosthodontic treatment is aimed at improving oral function, esthetics has become the most common motivation for treatment. To ensure successful outcomes, valid and reliable instruments for comprehensively evaluating the esthetic aspects of prosthodontic treatment from both clinician perspective and patient self-assessment are needed. The literature on measurement tools used in prosthodontics to evaluate orofacial esthetic aspects was also studied.
Methods:
A scoping review was conducted to map existing instruments such as a questionnaire, index, or scale designed to evaluate orofacial esthetics by clinician and patient for prosthodontic treatment.
Results:
Of the 27 studies evaluated, the Orofacial Esthetic Scale (OES) was used mostly for evaluating a patient’s esthetic perception. The ‘Dental Esthetic Screening Index’ (DESI) was found as the most currently developed instrument with objective quantification for the clinical situation having good reliability and validity. The Prosthetic Esthetic Index (PEI) also has sufficient psychometric properties as an objective assessment tool for clinicians. But the PEI and the DESI are still rarely used in research and practice. Teeth color and position were determined to be the most important factors in recognizing esthetic impairment. Following tooth analysis (appearance, color, alignment, space, proportion, and wear), gingival appearance, smile analysis, facial analysis, and unaesthetic restoration or prosthesis were the most important esthetic factors identified.
Conclusion:
Esthetics is subjective and is influenced by many factors. Instruments for subjective and objective evaluation are needed to determine the esthetic perceptions of clinicians and patients. OES, PEI and DESI were found to be relevant instruments for this.
1. INTRODUCTION
Prosthodontics is an area of dentistry focused on improving oral function and esthetics. Prostheses are used not only to restore partial and total edentulism but also to restore tooth damage. Thus, they must achieve harmony in shape and color with the lips, gingiva, smile, and face. Nowadays, esthetic considerations are the most common motivation for patients seeking prosthodontic treatment. The term orofacial is used in this study because it describes a particular region of the body consisting of the face, mouth, teeth, including lips, while gingiva is a more suitable term to evaluate comprehensive esthetic in prosthodontics [1]. The esthetic concept in prosthodontic refers to the definition of esthetic in dentistry, which is the theory and philosophy that deal with beauty and the beautiful, especially with respect to the appearance of dental restoration, as achieved through its form and or color; those subjective and objective elements and principles underlying the beauty and attractiveness of an object, design, or principle [2]. An essential consideration in the pursuit of orofacial esthetics is the concept of body image, defined as each individual’s mental picture of his or her appearance. The role of esthetics in prosthodontic treatment is strongly related to the individual's self-esteem, psychosocial perspective, and, ultimately, his/her quality of life [3, 4]. Therefore, esthetic interpretation during oral reconstruction should not be simply a subject of personal taste, from either the clinician’s or patient’s point of view. The patient’s perception of his/her oral health status, including esthetic perception as a subjective measure, is a significant component for measuring treatment outcomes [5]. This subjectivity makes the assessment of esthetics challenging because the final result has to satisfy the patient’s esthetic perception, which should be one of the outcomes measured in prosthodontic treatment [6].
Clinical assessment is an important process to ensure successful prosthodontic treatment outcomes. Generally, esthetic analyses of prosthodontic treatment consist of several parameters, including facial, dentolabial, tooth, gingival, and smile analyses [7, 8]. Some experts have separated dental and facial esthetics into macroelements and microelements [9]. A previous study established seven quantifiable parameters for orofacial esthetics from a literature review: smile line, lip line, incisal offset, location of the dental and facial midline, incisor angulation, and width-to-height ratio of anterior maxillary teeth, gingival contour and root coverage, and papilla height [10]. However, there are no specific esthetic guidelines developed by a consensus of esthetic experts and the clinical evaluation; therefore, it often varies.
Esthetic perception is subjective for both clinicians and patients. Age, gender, and psychosocial factors influence patients’ perception and both gender and culture have been reported to influence the clinician’s judgment of esthetics [11]. The esthetic conception is abstract and subjective; therefore, formulating a concrete treatment goal and good communication between dentists and patients is essential. Valid and reliable instruments are needed to systematize and accelerate this process. The purpose of this study is to review the published literature assessing the valid and reliable standardized instruments used in prosthodontics to evaluate orofacial esthetics by clinicians and patients. This study also aims to determine the orofacial esthetic aspects evaluated by patients and clinicians using existing measuring instruments.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
A scoping review was performed to identify the instruments that currently exist for assessing orofacial esthetic aspects and to investigate the elements that play a role in both the patient's perception and the clinician’s evaluation in prosthodontics. Scoping reviews are useful for mapping, collating, and summarizing existing literature on a topic and can assist researchers in identifying the nature and extent of the current research evidence [12-14]. Scoping studies differ from narrative or literature reviews because the scoping process requires analytical reinterpretation of the literature. Unlike the systematic review that might typically focus on a well-defined question where appropriate study design can be identified in advance, a scoping study tends to address broader topics where many study designs might be applicable. The systematic review might aim to provide answers to questions from a relatively narrow range of quality assessed studies, while a scoping study is less likely to seek to address very specific research questions nor, consequently, to assess the quality of included studies. The scoping review was chosen for this study because we need to identify and map the available evidence with a broader scope in a structured process that fulfils our study purposes. The five stages of the scoping review consist of identifying the research question, identifying relevant studies, study selection, charting the data, and collating, summarizing, and reporting results [12]. “What instruments are currently available to measure esthetics in prosthodontics?” was the question used as a guide for literature searches.
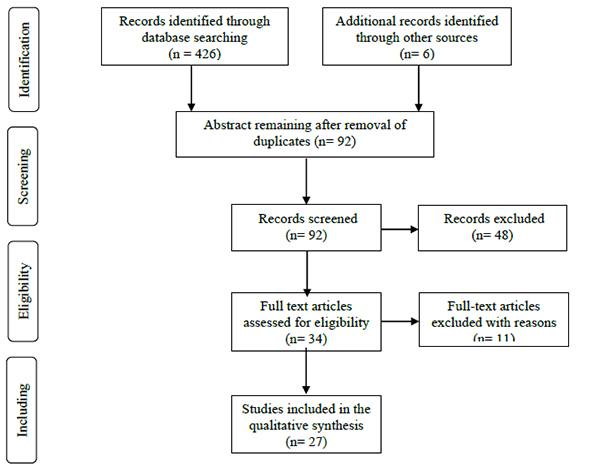
The approach to searching for this review followed the steps method recommended for systematic review using Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) flow diagram (Fig. 1).
The review focused on all available published English-language studies from the last 15 years. The PubMed, EBSCO, Pro Quest, and Google Scholar databases were searched using terms from Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) 2016 and other terms. The search strategy included combinations of the following MeSH terms: dental esthetics, perception, self-assessment, questionnaires, and scales to expand search coverage. Other keywords such as dentofacial esthetics, orofacial esthetics, dental appearance, satisfaction, and smile esthetics, were also used to find potentially eligible studies to be included in the review. The selected articles were screened by title and abstract. Studies related to orthodontics, malocclusion, and cleft abnormalities, as well as studies related to prosthodontics performed without using instruments such as questionnaires, scale, or index to assess esthetics were excluded from the study. Articles on implant research were not included because the assessment of implant esthetics mostly evaluates specific micro esthetic parameters [15]. The article selection process is described with the inclusion and exclusion criteria in Table 1.
3. RESULTS
This study adapted the search strategy method from Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis statement’s flowchart [16] (Fig. 1). After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria to the titles and abstracts of the 92 articles found with the aforementioned search terms, 27 full-text articles were considered suitable for further analysis.
Tables 2 and 3 describe the instruments available from 2006 until 2020, representing the chronological overview of orofacial esthetic instruments for self-evaluation by the patient, and clinician evaluation.
The esthetic aspects of each instrument were evaluated, as well as their measurement method and psychometric properties. The studies were charted, and summaries were drafted, including the author, journal, publication year, aim, sample, and the instrument used. Table 4 summarizes the instruments identified through the scoping review.
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Period | From April 2006 to January 2020 | Outside the date range |
| Language | English | Non-English |
| Article Type | Original article, Clinical research | Not original research, peer-reviewed journal article and or unpublished |
| Subjects | Adults (18 years old and above) | Children (under 18 years old) |
| Study focus | Instruments that evaluate orofacial esthetics in prosthodontics or restorative dentistry, and patient satisfaction with dental appearance | Orthodontic scales and indexes, Orthodontic malocclusion, Quality of life questionnaires, Assessment by a Layperson, Cleft lip or cleft palate, Dental implants |
| Authors and Year | Name of Instrument | Items | Response | Psychometric Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wolfart et al. 2006 | Participants’ satisfaction with dental appearance questionnaire | Maxillary anterior teeth (length and harmony); Teeth (exposure while smiling, spacing, midline, appearance, position, proportion, color, unpleasant condition); Others (gum visibility, wish for different teeth, hiding teeth, feel old because of teeth) | Five-point Likert scale | Not available |
| Samorodnitzky-Naveh et al. 2007 | Questionnaire of dental satisfaction | Patient satisfaction with dental condition; Teeth overall (appearance, color, crowding, alignment, protrusion); Anterior teeth (nonesthetic restoration, fracture); Others (hiding teeth while smiling); Satisfaction with previous esthetic treatments; Orthodontic treatment, teeth whitening; Anterior teeth (crowns, implants, root canal); Desired esthetic dental treatments; Teeth (general appearance improvement, whitening, alignment, anterior teeth crown) | Yes/No | NA |
| Tortopidis et al. 2007 |
Self-evaluation questionnaire of esthetic treatment need | Self-evaluation of esthetic perception (12 items): Smile, embarrassed about teeth condition, teeth color, gingival inflammation, the shape of upper central teeth, visible gum, teeth malposition, smile appearance, esthetic treatment need. |
Yes/No | Good reliability in internal consistency test |
| Mehl et al. 2009 |
Questionnaire of Satisfaction with Own Dental Appearance | Teeth (appearance, size (width and length), color, position, shape); Others (gum appearance, dissatisfaction with artificial teeth, dissatisfaction with teeth spacing, hiding teeth, wish for different teeth, feel old because of teeth) | Five-point Likert scale | NA |
| Larsson et al. 2010 | Orofacial Esthetic Scale | Facial appearance, facial profile, mouth appearance, rows of teeth, the color of teeth, teeth shape/form, gingiva, the overall impression | Ten-point Likert scale | Test-retest reliability, internal consistency, content-discriminant-convergent validity |
| Tin-Oo et al. 2011 | Questionnaire of patient satisfaction and desired treatment to improve esthetics | Questionnaire about patient satisfaction with current dental appearance: Teeth overall (appearance, color, crowding, alignment, protrusion, fracture); Anterior teeth - caries, nonesthetic restoration; Desired esthetic treatment need (Orthodontic treatment, crowns, teeth whitening, teeth color restorations, and partial dentures) | Yes/No | NA |
| Authors and year | Name of Instrument | Items | Response | Psychometric Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tortopidis et al. 2007 [17] | Professional assessment questionnaire of esthetic treatment need | Dentofacial analysis (Upper lip line, smile width, central incisor midline coincides with filtrum, upper midline coincides with lower midline); Dental analysis (Proportion of central incisor, angle classification, skew); General information (Gingiva: height asymmetry, discoloration, inflammation; Teeth - crowded, rotated, spaced teeth, occlusal wear, discolored, over-contour restoration, margin restoration, discolored fixed restoration, discolored fillings, chipped or fracture restoration) | Yes/No | Good reliability (Cronbach alfa = 0.82) |
| Özhayat et al. 2014 [18] | The Prosthetic Esthetic Index (PEI) | Thirteen items on oral facial, prosthetic and dental esthetic aspects: Facial asymmetry, dental arch symmetry, teeth spacing, morphology, color, position, spacing/crowding, the margin of fixed dental prostheses, discoloration, the color of gingiva, retraction of the gingiva, teeth wear, overall esthetic evaluation of the patients | Five-point Likert scale | Valid and reliable (test-retest, internal consistency, inter-rater reliability test, content validity, criterion validity, construct validity, sensitivity test) |
| Rotundo et al. 2015 [19] | The Smile Esthetic Index (SEI) | Smile line, facial midline; Teeth (alignment, deformity, discoloration); Gingiva (discoloration, recession, excess, gingival scars, diastema) | Yes/No | Reproducible and reliable tool for assessing esthetic components of a smile. Psychometric test: Inter-rater agreement and intra-rater agreement. |
| Frese et al. 2019 [20] | The Dental Esthetic Screening Index (DESI) | Five items on the extraoral aspect: facial and dental midline congruency, angulation between upper incisor and facial midline, the parallelism of canine line and pupillary line, expose upper teeth during smile and parallelism of the smile line. Seven items in intraoral aspects: gingival contour, interdental papilla position, continuity of upper dental arch, upper teeth angulation, proximal contacts, tooth color and width-height-ratio of the upper central incisor |
5 point rating scale | Valid and reliable (Psychometric test: inter-and intra-rater reliability, clinical validation with comparison before and after treatment) |
| Authors & Year | Title and Journal | Aims | Sample | N | Instruments Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wolfart et al. 2006 [21] | General well-being as an important co-factor of self-assessment of dental appearance (Int J Prosthodont) | To correlate the general well-being of patients with judgment about the dental appearance | 19–79 yr old with natural dentition, fixed partial dentures, removable partial dentures, dental esthetic problems | 80 | Dental appearance satisfaction questionnaire |
| Samorodnitzky-Naveh et al. 2007 [22] | Patients’ satisfaction with dental esthetics (J Am Dent Assoc) | To evaluate factors influencing patient satisfaction with dental appearance and with the results of esthetic treatment | NA | 407 | Dental satisfaction questionnaire |
| Tortopidis et al. 2007 [17] |
Evaluation of the relationship between subjects’ perception and professional assessment of esthetic treatment needs (J Esthet Restor Dent) | To examine the relationship between Greek subjects’ perception and professional assessment regarding the need for esthetic dental treatment | 17–65 yr old (a military dental clinic in Tel Aviv, Israel) | 132 | Professional assessment questionnaire of esthetic treatment needs. Self-evaluation questionnaire of esthetic treatment need |
| Mehl et al. 2009 [23] | Does the Oral Health Impact Profile Questionnaires measure dental appearance? (Int J Prosthodont) | To evaluate whether there is a need to develop a new questionnaire measuring dental appearance or if this is already covered by the OHIP-49 | 49–69 yr old | 30 | QDA, OHIP-49, OHIP-esthetic |
| Larrson et al. 2010 [1] | Development of an Orofacial Esthetic Scale (OES) in prosthodontic patients (Int J Prosthodont) | To develop a self-reported orofacial esthetics instrument, OES, addressing prosthodontics concerns | Prosthodontics patients at the Center of Oral Rehabilitation Linkoping, Sweden | 119 | OES |
| Larsson et al. 2010 [24] | Reliability and validity of the Orofacial Esthetic Scale in Prosthodontic Patients (Int J Prosthodont) | To evaluate the reliability and validity of OES | 22-70 yr old (esthetic & functional) & healthy control groups (esthetic control & functional control) | 119 | OES |
| Persic et al.2011 [25] | Psychometric Properties of the Croatian version of the Orofacial Esthetic Scale and suggestion for modification (Int J Prosthodont) | To develop and test the psychometric properties of OES Croatian version | Subjects were divided into four groups that included two patient groups (esthetic normal but functionally impaired & esthetically impaired) & healthy control groups (esthetically normal control & esthetically impaired control) | 126 | OES |
| Mehl et al. 2011 [11] | Patients’ and dentist’s perception of dental appearance (Clin Oral Investig) | To compare self- & professional perception of complex oral rehabilitation. To evaluate the experience, age & gender-related differences in professional judgment | 63±9 years old. Patients had been treated in a student course at the Department of Prosthodontics, Germany | 16 patients, 42 dentists |
QDA |
| Mon Tin-Oo et al.2011 [26] | Factors influencing patient satisfaction with dental appearance & treatments they desire to improve esthetics (BMC Oral Health) | To identify patient satisfaction with general dental appearance, cosmetic elements & desired treatments | Patients newly registered at HUSM Dental Clinic, Malaysia. Adults >18 years old who had not received any dental treatment within the last six month | 243 | Patients’ satisfaction with current dental appearance & desired esthetic treatment needs questionnaire |
| John et al. 2012 [27] | Validation of the Orofacial Esthetic Scale in the general population (Health Qual Life Outcomes) | To assess how patients perceive their dental & facial, and to investigate dimensionality, reliability, & validity of OES scores in the Swedish adults | 32–66 years old. Swedish-speaking subjects, 18 years old or older | 1159 | OES |
| Al-Zarea 2013 [28] | Satisfaction with the appearance and the desired treatment to improve esthetics | To investigate participant satisfaction with the appearance of their teeth and the desired treatments to improve dental appearance | Participants above 18 years old had no medical disease or condition that might affect their ability to understand and score the questionnaire, and received no dental treatment for the last 6 months. | 220 | Patients’ satisfaction with current dental appearance & desired esthetic treatment needs questionnaire |
| Zhao et al. 2013 [29] | Development of the Chinese version of the Orofacial Esthetic Scale (J Oral Rehabil) | To investigate the psychometric properties of OES among Chinese speaking patients | 56.2 ± 16.2-year-old prosthodontics patients at Hospital Medical University, China. Subjects were divided into four groups: Patient groups (esthetic normal but functionally impaired & esthetically impaired) & healthy control groups (esthetically normal control and esthetically impaired control) | 202 | OES |
| Ozhayat et al. 2014 [18] | Validation of the Prosthetic Esthetic Index (PEI) (Clin Oral Investig) | To validate a new comprehensive index, the Prosthetic Esthetic Index (PEI), for a professional evaluation of esthetics in prosthodontics patients | Participants were patients missing at least one tooth (3rd molar not included) & registered for oral rehabilitation at the Department of Odontology, University of Copenhagen | 99 | PEI |
| Carlsson et al. 2014 [30] | Orofacial Esthetics and dental anxiety: Associations with oral and psychological health (Acta Odontol Scandinav) | To investigate self-rated orofacial esthetics in patients with dental anxiety & its relationship to psychological & oral health | 20–81 ys old patients who were referred to a dental anxiety specialized clinic, University of Gothenburg, Sweden | 152 | OES |
| Mehl et al. 2014 [31] | Perception of dental esthetic in different cultures (Int J Prosthodont) | To compare patients’ & dentists’ perceptions of dental appearance | 22–67-year-old patients at a private practice in London | 29 patients 94 dentists |
QDA |
| Danneman et al. 2014 [2] | Recognition of patient-reported impairment in oral aesthetics (J Oral Rehabil) | To investigate the degree of effective recognition by professionals of patient-estimated oral esthetic impairment & the most reliable aspects in such recognition | Patients missing at least one tooth (3rd molar not included) & registered for oral rehabilitation at the Department of Odontology, University of Copenhagen | 99 | PEI, OES Oral Health Impact Profile Aesthetics (OHIP-Aes) |
| Reissmann et al. 2014 [32] | Development and validation of the German version of OES (Clin Oral Investig) | To develop a German version of OES and to assess its psychometric properties | 41-70 yr old patients recruited at the Department of Prosthetic Dentistry, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Germany with or without dental treatment need. Not based on esthetic concern, only on clinical consideration | 165 | OES |
| Rotundo et al. 2015 [19] | The Smile Esthetic Index (SEI): A method to measure the esthetics of the smile. An intra & inter-rater agreement study (Euro J Oral Implantol) | To propose a method to measure the esthetics of the smile & to report its validation by means of intra & inter-rater agreement | Frontal pictures of smiles of patients from 19–61 years old | 70 patients 10 examiners |
SEI |
| Bimbashi V et al. 2015 [33] | Psychometric properties of the Albanian version of the Orofacial Esthetic Scale (OES-ALB) (BMC Oral Health) | To adapt OES & test psychometric properties of the Albanian version in the Republic of Kosovo | 19–86 years old (prosthodontics patients without treatment need, with treatment need, dental students with natural teeth without treatment need | 169 | OES |
| Wetselaar P et al. 2015 [34] | Psychometric properties of the Orofacial Esthetic Scale (OES-NL) Dutch version in dental patients with & without self-reported tooth wear (J Oral Rehabil) | To test the psychometric properties of the Dutch version of OES in dental patients with & without self-reported tooth wear | Adult patients referred to the Clinic of Orofacial Pain and Dysfunction because of temporomandibular disorder, dental sleep disorder & tooth wear | 583 | OES |
| Persic and Celebic 2015 [35] | Influence of different prosthodontics rehabilitation option on Oral Health-related Quality of Life, Orofacial Esthetics and Chewing Function based on patient-reported outcomes (Qual Life Res) | To assess the influence of different prosthodontics rehabilitation options on improvement of orofacial esthetics, chewing function, and oral health-related quality of life | Patients who were treated either with conventional or implant-supported dentures at the Prosthodontics Department, School of Dental Medicine, University of Zagreb. | 263 | OHIP, OES and Chewing Function Questionnaire (CFQ) |
| Ozhayat et al. 2016 [36] | Responsiveness of the Prosthetic Esthetic Index (Clin Oral Investig) | To evaluate the responsiveness of the Prosthetic Esthetic Index (PEI) | Adult patients at the Prosthodontics Department, University of Copenhagen before & after treatment | 57 | OES & PEI |
| Alhajj et al. 2016 [37] | Development, validation and psychometric properties of the Arabic version of the Orofacial Esthetic Scale: OES-Ar (BMC Oral Health) | To develop the Arabic version of the OES (OES-Ar) and to investigate its psychometric properties among Arabic-speaking populations with and without esthetic impairment. | Participant aged 18 years and older recruited from conservative and prosthodontics department at faculty of dentistry, Thamar University, and private dental clinics | 230 | OES |
| Oreški et al. 2017 [38] | Assessment of esthetic characteristic of the teeth and surrounding anatomical structure (Acta Stomatol Croat) | To determine differences between general population, dentists & prosthodontics specialists, and to determine the difference in their perception of anterior teeth anatomical variations & surrounding structures based on the gender & age of the assessor | 19–40 yr old. Participants had a permanent fully toothed dentition (excluding 3rd molars) & mostly intact upper front teeth. All respondents belonged to the Angle class I | 60 | OES |
| Aldaij et al. 2018 [39] | Patient satisfaction with dental appearance and treatment desire to improve esthetics (J Oral Health Comm Dent) | To evaluate the patient's satisfaction with dental appearance and treatment desire to improve esthetics. | Adult patient (18 years and above) who attended to the department of university dental clinic of Riyadh Elm University, Saudi Arabia | 1147 | Patients’ satisfaction with current dental appearance & desired esthetic treatment need questionnaire |
| Pallares et al. 2018 [40] | Development, validity and reliability of the Orofacial Scale-Spanish version (J Prosthodont Res) | To develop a Spanish version of the Orofacial Esthetic Scale (OES-Sp) and to determine psychometric properties in dental patients. | The Spanish-speaking participant from Healthpertners dental clinic (age mean± sd: 42,9± 12,3 years) | 331 | OES, OHIP |
| Reissman et al. 2019 [41] | Measuring patient’s orofacial appearance. Validity and reliability of the English-language Orofacial Esthetic Scale (JADA) | To determine the psychometric properties of the English-language version of OES-E in a population of the dental patient | 56.7±15.8-year-old English dental patients from Health Partners dental clinic in Minnesota, USA | 1784 | OES |
4. DISCUSSION
The success of prosthodontics treatment not only restores the function of the stomatognathic system but also provides a pleasing and esthetic appearance of restoration in harmony with the whole body. Clinical experiences and research showed that patients’ opinions of esthetic parameters often were different from clinicians. Even though it is not easy to measure because it is influenced by several factors such as age, gender, education level, and culture, the assessment has to be done. There are several ways to measure the patient’s self-perception of orofacial appearance; first is the satisfaction of orofacial esthetic appearance; second is the impact of its impairment, which is strongly related to the psychosocial quality of life [26, 28, 42, 43]. These two methods also can be assessed in different periods of time; existing condition/previous dental treatment and after receiving treatment. In this review, we only analyzed instruments to evaluate the patient perception of orofacial appearance. In this scoping study, we found four instruments for assessing the patient's perception of orofacial aesthetic, which include the prosthodontic aspect. The measurements used by Tortopidis et al., Tin-Oo et al., Questionnaire Satisfaction with their own dental appearance' (QDA) and Orofacial Esthetic Scale (OES). The patients’ satisfaction regarding their orofacial condition was asked in all the instruments. All self-assessment instruments investigated the impact of esthetic impairment and or the desired treatment needed to overcome the problem, except the OES. The OES instead evaluates the overall satisfaction of the patient with his/her esthetic appearance. As the most common instrument used in research, the OES has good psychometric properties and has been adapted cross-culturally to several languages such as; Croatia, Chinese, Albanian, Dutch, Germany, Arabic, and Spanish [25, 29, 32-34, 37, 40, 41]. Although the instrument developed by Tortopidis et al. showed good reliability, there has been no report of its use in other published studies. The QDA was developed from an earlier version by Wolfart et al. [21]. Mehl et al. reintroduced it with the name of QDA in a shorter version and used several times to assess the perceptions of aesthetics for their research [11, 23, 31, 44]. Even though used by Mehl et al., the QDA has not been proven to be valid and reliable, the scoring method and its interpretation are not explained in the published articles. Other instruments identified were questionnaires for patient satisfaction with esthetics and the need for dental esthetic treatment.
In this study, we recognized that there are several clinical measurements for assessing the aesthetic orofacial that includes the prosthodontic aspect. Tortopidis et al. made a questionnaire with the aesthetic aspect of prosthodontics covered by the measurement, but the interpretation of the summary score and its reliability was not reported [17]. Another measurement is the Smile Esthetic Index (SEI); it also has some prosthodontic aesthetic aspects associated with the overall smile assessment [19]. This tool demonstrates the value of good agreement on inter-rater and intra-rater reliability tests but has not been reported in clinical or other studies. Esthetic evaluation instruments that have been tested for validity and reliability for prosthodontic cases are Prosthetic Esthetic Index (PEI) and also have good responsiveness [18, 36]. Developed by Ozhayat et al., this tool is for clinicians in daily practice or research because it considers structured aspects which include aesthetic prosthetic aspects of the face, mouth, prosthetic, and comprehensive dental aesthetic. PEI questionnaires have been reported to have been used in studies for assessing orofacial aesthetic impairment in prosthodontic [2]. The most current tool found was the ‘Dental Esthetic Screening Index’ (DESI) developed by Frese et al. in 2019, based on their review findings in 2012. The DESI was found to be a reliable and valid instrument for the quantitative assessment of dentofacial esthetics.
The ‘Professional assessment questionnaire of esthetic treatment need’, the PEI, and the SEI, although assessed clinically, remain influenced by the subjectivity of the clinician. However, this method is an effective way of evaluating because it is easy and fast in assessing an aesthetic disorder rather than a measurable objective examination. The scoring method, clinician’s experience, previous dental education, and culture can influence the clinician’s assessment [25, 31, 35, 44]. Guidelines to determine a scoring scale, such as that included in SEI, may help reduce subjectivity. Dichotomous questions, yes/no answers are easy to answer, but in terms of analysis, such questions will only separate respondents into two broad groupings, and finer comparisons are usually required. Likert scale questions and semantic differentials to measure attitude respondent towards perception, feeling, or opinion can indicate responses by the degree of positive and negative statements. Both Likert scale and semantic differentials usually incorporate'odd-numbered' steps and creating mid-point, which gives the respondent a choice to neither agree nor disagree [45]. These should be considered because some respondents have the tendency to be ambivalent. The number of Likert scale choices and the selection of words such as always, often, seldom or sometimes might affect the pattern of the responses with different cultural backgrounds [46]. In comparison, the DESI would provide a comprehensive index that allows for objective quantification of the clinical situation for reliable baseline and outcome assessment in esthetic dentistry compared with the PEI, the SEI, and the questionnaire of professional assessment. Extraoral and intraoral scores of the DESI quantification were done by a five-point rating scale that allows for stepwise gradation of the esthetic deviance to ideal.
The instruments identified in this review use a variety of esthetical aspects to determine the patient’s perception and the clinician’s evaluation. All instruments were found to cover all the aspects of prosthodontics esthetic analysis recommended in several references, including facial, dentolabial, tooth, gingival, and smile analyses. Tooth color and position were found to be the most important factors in recognizing esthetic impairment [26, 28, 42]. Similar results have been reported by Dannemand et al., Somorodnitzki et al., and Oo et al. Tooth analysis (appearance, color, alignment, space, proportion, and wear), gingival appearance, smile analysis, facial, and unesthetic restoration or prosthesis were identified as important esthetic factors in this review.
These findings showed that scoping studies can provide an important result from the research question presented in this study. It can be useful as a starting point, based on the evidence to decide for the relevant instrument in esthetic prosthodontics research. As the limitation of this study, we found it very challenging to identify the relevant study with the resources available. But the recommendation step suggested by Levac et al. [13] to involve at least two independent researchers and a reviewer to determine agreement in every stage surely solved the problem.
Furthermore, this finding can give preliminary results to conduct a systemized and comprehensive study to legitimize the best instrument for esthetic evaluation. The comprehensive and ideal criteria for the good instrument properties from the Scientific Advisory Committee (SAC) of the Medical Outcome Trust should include eight attributes; conceptual and measurement model, validity, reliability, responsiveness, interpretability, respondent and administrative burden, alternative forms and cultural and language adaptation [47].
CONCLUSION
Esthetics is subjective and is influenced by many factors. Instruments for subjective and objective evaluation are needed to determine the esthetic perceptions of clinicians and patients. OES is the most widely used instrument for self-evaluation in orofacial esthetics research. The PEI and the DESI were identified as the quantifiable valid and reliable tools used for orofacial esthetic evaluation by the clinician.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
FUNDING
The publication of this manuscript is supported by the Universitas Indonesia Grant No. NKB-0413/UN2.R3.1 /HKP.05.00/2019.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The author declares no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Declared none.


